 Mysteries
Mysteries  Mysteries
Mysteries  History
History 10 Surprising Stories About the Texas Rangers
 Humans
Humans 10 Philosophers Who Were Driven Mad by Their Own Theories
 Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous 10 Video-Game-Worthy Weapons and Armors from History
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Psychics Who Accurately Predicted Wartime Events
 The Arts
The Arts 10 Pieces of Art Inspired by a Broken Heart
 Health
Health 10 Science Fiction-Sounding New Medical Treatments
 History
History 10 Surprising Facts About the Father of Submarine Warfare
 Space
Space Ten Astonishing New Insights into Alien Worlds
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Bizarre Summer Solstice Rituals Still Practiced Today
 Mysteries
Mysteries Top 10 Haunting Facts About the Ghost Ship MV Alta
 History
History 10 Surprising Stories About the Texas Rangers
 Humans
Humans 10 Philosophers Who Were Driven Mad by Their Own Theories
Who's Behind Listverse?

Jamie Frater
Head Editor
Jamie founded Listverse due to an insatiable desire to share fascinating, obscure, and bizarre facts. He has been a guest speaker on numerous national radio and television stations and is a five time published author.
More About Us Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous 10 Video-Game-Worthy Weapons and Armors from History
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Psychics Who Accurately Predicted Wartime Events
 The Arts
The Arts 10 Pieces of Art Inspired by a Broken Heart
 Health
Health 10 Science Fiction-Sounding New Medical Treatments
 History
History 10 Surprising Facts About the Father of Submarine Warfare
 Space
Space Ten Astonishing New Insights into Alien Worlds
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Bizarre Summer Solstice Rituals Still Practiced Today
10 Incredible Recently Discovered Animals
Most of us share a fascination with the unknown. Thanks to this – as well as tremendous advances in technology – most of our planet has been quite thoroughly examined. Some areas remain, however, which are home to creatures that science has yet to encounter.
Recently discovered animals number in the thousands. Thus far, 1.8 million unique species have been documented; it’s estimated that more than ten million species remain to be found. Most newly discovered creatures are minute organisms of little interest; some, however, are creatures of immense interest, which simply eluded us for quite some time. The following list is comprised of ten such animals.

I’ve opted to put this monstrous creature at number ten for one very simple reason: it terrifies me. It terrifies me so much that I didn’t want to grant it the honour of placing it any higher. The species was officially discovered in 2006 during an expedition to Guyana. It is a burrowing spider, feeding primarily on invertebrates, though it has also been observed eating small mammals, lizards, and venomous snakes (surprise surprise). Fully grown specimens can reach a horrific weight of around six ounces. Thankfully for us – and for any other creatures too large for the spider to eat – the goliath bird eater is a species of tarantula, and has relatively weak venom, which causes mild swelling and pain for a few hours.
But the thing that poses the biggest threat to us humans is the goliath’s ability to expel urticating hairs from its body. These tiny, nearly invisible hairs float through the air – and have an awful tendency to stick in the eyes.
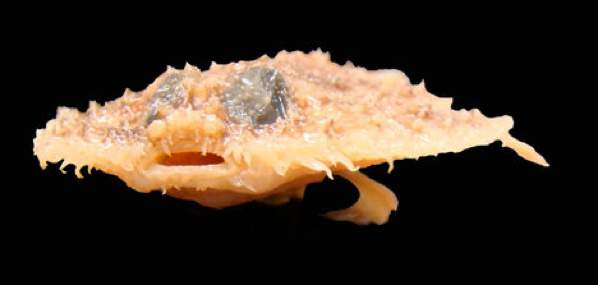
Belonging to the Ogcocephalidae family of batfish, the Louisiana pancake batfish is a bizarre looking creature native to the Gulf of Mexico. The species was discovered in 2010, during the cleanup process following the infamous oil spill in the gulf, which affected every kind of batfish.
The Louisiana pancake batfish’s name comes from its shape, which quite closely resembles that of a horrendously prepared pancake. The strange manner it has of moving along the ocean floor is described as being similar to the way a bat crawls. The pancake batfish feeds on invertebrates, which it uses chemical lures to capture.
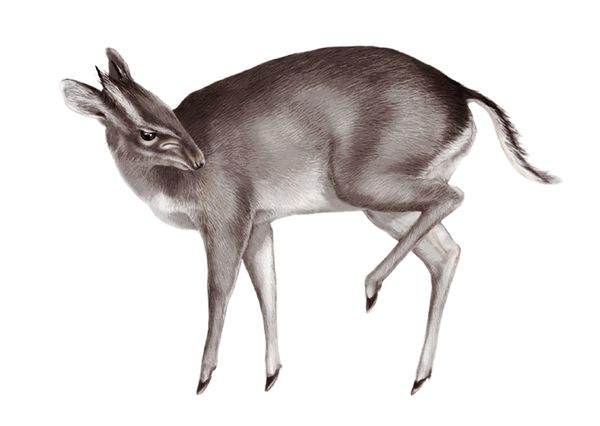
Walter’s Duiker is a fascinating little creature, officially discovered in 2010 in the Dahomey Gap, West Africa. The species made its first foray into the world of science in 1968, when Walter Verheyen – the man after whom the species is named – retrieved a specimen in Togo. This species of duiker is native to Togo, Benin, and Nigeria.
One of the most interesting characteristics about the species is its small stature, measuring an average of only forty centimeters (sixteen inches) in height and typically weighing four to six kilograms. In addition to its small height, the duiker has hind legs which are longer than their counterparts up front. This is particularly interesting given that the duiker is not a grazing animal, and typically feeds on berries and other similar items of nourishment, which grow on plants.

This rather snuggly looking crustacean was discovered in 2005 in the South Pacific Ocean. Given the presence of a substantial quantity of silky blond setae, its discoverers were quick to dub it the ‘yeti crab’. The unusual little decapod reaches an average length of around fifteen centimetres (just under six inches) and lives around hydrothermal vents deep in the ocean. It is for this reason that the fur-like setae contain filamentous bacteria, which allow the creature to detoxify poisonous substances emitted in the water by vents. It has been speculated that the yeti crab may actually feed on such bacteria – but it is generally believed to be a carnivore.
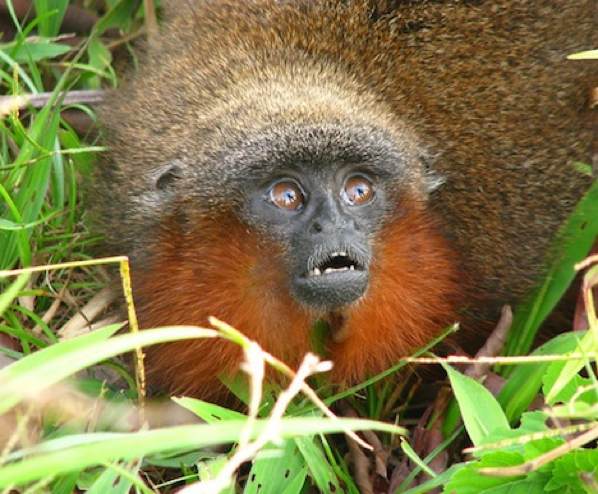

The red-bearded titi is a small primate discovered in the Colombian section of the Amazon Rainforest in 2008. Unfortunately, the story of the discovery is not all happy, as it appears the adorable bearded little things are critically endangered, with an estimated surviving population of less than 250. The red-bearded titi, like many primates, shares a surprising number of characteristics with humans. One such characteristic is that they mate for life – an uncommon habit in the primate world. A typical couple has a baby every year, and males are responsible for a majority of the infant’s care. Couples have often been seen sitting together on tree branches with tails intertwined.
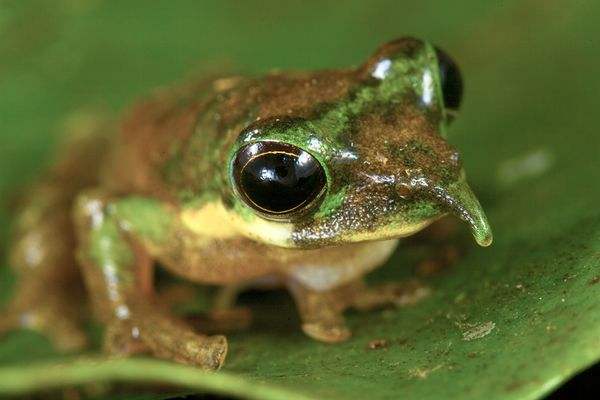

Found in the remote Fuja Mountains of Indonesia, the Pinocchio frog is a strange little creature which was only discovered by accident in 2010, after wandering into a research camp and perching itself atop a bag of rice. The animal’s most obvious distinctive feature is the odd protuberance on the front of its face – most often referred to as its nose. The strange nose-like thing is a feature which only the males have, and becomes erect when they are making excited calls, returning to its standard position when they are not. The exact purpose of the ‘nose’, and the frogs’ ability to manipulate it, is as yet unknown.
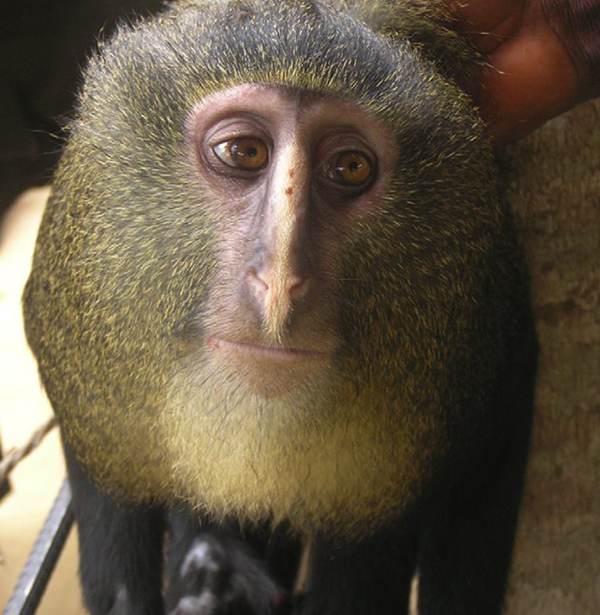

The lesula is a remarkable new species of African monkey discovered in 2007. It was discovered in the Democratic Republic of Congo and is the second new species of African monkey discovered in nearly three decades. The monkey was first seen (by non-locals) in 2007 by John and Terese hart of Yale University’s Peabody Museum of Natural History, in the home of a primary school teacher in the town of Opala. The most visible characteristic which makes the lesula so unusual is its startlingly human face. A slightly less obvious characteristic are the bald patches on the monkey’s hindquarters and genital region, both of which are coloured a vibrant blue.

The wattled smoky honeyeater is a species of honeyeater endemic to the Foja Mountains of Indonesia. This particular species’ most distinctive feature is the reddish-orange facial skin around its eyes. Discovered in December of 2005, the wattled smoky honeyeater was the first new bird species discovered in New Guinea since 1939. In addition to the brilliant orange skin around the bird’s eyes, it has the curious characteristic of walking with a ‘wottle’. The honeyeater was one of over twenty new species discovered in a single expedition that took place in 2005. The shade of the bird’s facial skin changes slightly when flushed.
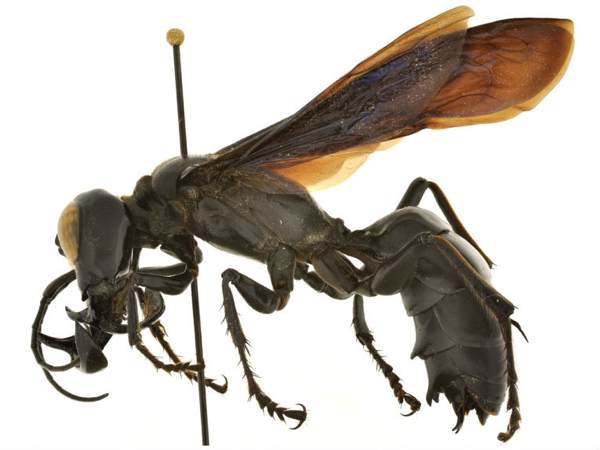

I’ve already mentioned a number of recently discovered animals from Indonesia – and I would gladly wager that this is the most terrifying of the lot. The megalara garuda, also known (for good reason) as the king of the wasps, is an enormous wasp officially discovered in the Mekongga Mountains on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi in 2011. Average males are about two inches in length, and have an elongated mandible similar in size to their forelegs. Not only is the megalara garuda massive and demonic looking – it is also venomous. The first specimens of the wasp were collected on an expedition to Indonesia in 1930; however the first live specimen was captured and documented just last year. Much like many other rare species, deforestation and other environmental impacts pose a threat to the wellbeing of the species.
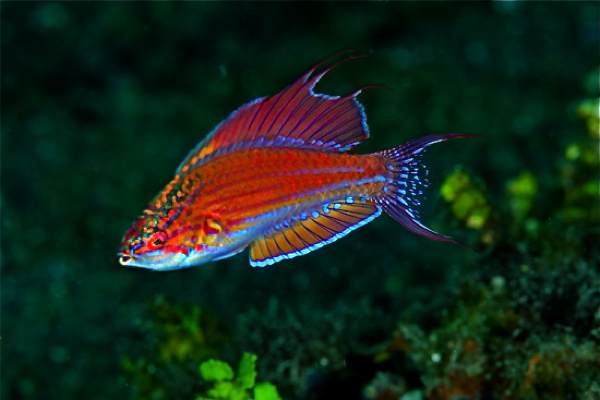

First described in 2008, paracheilinus nursalim is a new species of flasher wrasse discovered in the Bird’s Head Peninsula in Western New Guinea. The fish’s most distinctive characteristic is of course its incredibly bright, vibrant colours. Given the recent nature of its discovery, little is currently known of the creature.
To end on a cheery note: the future for the paracheilinus nursalim looks quite a lot brighter than can be said of some other animals on this list. The fish’s primary habitat is located within already-protected waters, meaning that it’s safe from external factors which may otherwise have put it at risk.








