Crime
Crime  Crime
Crime  Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Movie Franchises That Started Dark but Turned Surprisingly Soft
 History
History 10 Wars That Sound Made Up (but Absolutely Happened)
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Movie Adaptations That Ruined Everything for Some Fans
 History
History 10 Dirty Government Secrets Revealed by Declassified Files
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Wacky Conspiracy Theories You Will Need to Sit Down For
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Weird Ways That TV Shows Were Censored
 Our World
Our World 10 Places with Geological Features That Shouldn’t Exist
 Crime
Crime 10 Dark Details of the “Bodies in the Barrels” Murders
 Animals
Animals The Animal Kingdom’s 10 Greatest Dance Moves
 Crime
Crime 10 Criminal Masterminds Brought Down by Ridiculous Mistakes
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Movie Franchises That Started Dark but Turned Surprisingly Soft
 History
History 10 Wars That Sound Made Up (but Absolutely Happened)
Who's Behind Listverse?

Jamie Frater
Head Editor
Jamie founded Listverse due to an insatiable desire to share fascinating, obscure, and bizarre facts. He has been a guest speaker on numerous national radio and television stations and is a five time published author.
More About Us Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Movie Adaptations That Ruined Everything for Some Fans
 History
History 10 Dirty Government Secrets Revealed by Declassified Files
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Wacky Conspiracy Theories You Will Need to Sit Down For
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Weird Ways That TV Shows Were Censored
 Our World
Our World 10 Places with Geological Features That Shouldn’t Exist
 Crime
Crime 10 Dark Details of the “Bodies in the Barrels” Murders
 Animals
Animals The Animal Kingdom’s 10 Greatest Dance Moves
10 Ways Life Really Sucked in the Middle Ages
The Middle Ages lasted a long time… and probably felt even longer. Historians generally recognize the period as beginning with the fall of Rome at the end of the 5th century AD. Then, it lasted all the way through the middle of the 15th century—give or take a few decades. As you might imagine, quite a few things changed during this long cultural epoch. But there was at least one constant then, too: life really, really sucked.
There were only a few hundred million people on the entire globe—with less than 25 million in Europe–when the Middle Ages started, and those poor souls had it rough. Medicine was essentially nonexistent, and disease was rampant. Life was short, violent, uncertain, and occasionally brutal. Work was hard, the hours were long, and the physical toll was demanding. Civilization was sputtering along, and if you weren’t rich royalty, you got the proverbial (and sometimes literal) short end of the stick.
So let’s head back in time and take a long look at why life in the Middle Ages was so terrible. There will be famine, pestilence, and disease. There will be violence, starvation, political strife, and community turmoil. And there won’t be much hope! Here are ten reasons why it was really, really bad to be an Average Joe during the Middle Ages.
Related: Top 10 Fascinating Medieval Artifacts
10 Pestilence and Plague
Back in 1347, the bubonic plague—which soon became known as the Black Death—arrived in Europe. It caused immense devastation almost immediately. Over the next decade, it took the lives of millions of people. Historians now estimate that around twenty million were felled by the disease. And there weren’t nearly as many people in Europe then to begin with as there are now. In just a few years, almost half of Europe’s population perished.
The Black Death was a merciless killer. People would go to sleep healthy at night, wake up deathly ill in the morning, and die in an agonizing way over the next several days. It didn’t discriminate between the rich and the poor, and it was ruthless. In fact, scientists now estimate that only about 10% of those who contracted the disease managed to survive. Families were devastated, and entire towns were nearly wiped off the map.
It changed the structure of European society in a way that is difficult to understand today. While the Middle Ages were already tough on regular people, all that death made things even more difficult. Children were orphaned, and families were fractured. Already nearly nonexistent social and community outlets were completely shuttered.
People were on their own even more than they’d been for centuries before that. And they attributed the plague’s wrath to a vengeful God hell-bent on punishing the world for its sins. It may have been difficult for the modern world to battle the COVID pandemic, but it was nothing compared to the plague. In just a few years, in the late 1340s, European society completely regressed.[1]
9 Live Terribly, Die Fast
As you’ve come to see by now, life was tough in the Middle Ages. Even if you managed to stay away from hunger and the awful Black Death, there were still many ways to meet a gruesome end. Diseases like tuberculosis, leprosy, and cholera were everywhere. Basic cleanliness was hard to find. Nobody knew anything about hygiene. And in cities like London, there was no sewer system to speak of. Instead of disposing of excrement and human waste in a sensible way, they simply threw it onto the streets. Gross, right? Not only did it stink horribly, but it also created a terrible breeding ground for deadly diseases.
Knowledge about medicine was remarkably primitive, too. People in those times believed bad smells directly caused diseases. This idea was called the Miasma Theory, and it became quite popular across Europe. Of course, it wasn’t true, but it did make people realize the importance of being clean and taking baths. That, in turn, helped improve health conditions a little bit. Of course, the improvement was not felt by all classes. Rich people had the means and opportunity to stay clean and smell relatively fresh if they wanted. But for the serfs, who usually lived in cramped spaces with multiple families and even livestock, it was much harder.
Surviving childhood was a challenge back then too. Only about a third of all kids born in that era reached adulthood. Giving birth was also extremely dangerous, as you might expect. Mothers, babies, or both often didn’t make it out of childbirth alive. Across society at that time, the average life expectancy was only around 35 years. Men usually lived a little longer than women—and the rich, of course, often lived much longer than the poor. Still, it’s pretty shocking that giving birth was more risky than going into battle during medieval times. Life was very, very hard back then![2]
8 The Relentless Waging of War
During the Middle Ages, there was a great deal of fighting happening pretty much all the time. Some wars were short and violent, while others, like the 100 Years’ War, lasted way longer than expected. Because militaries lacked modern weapons, it often took decades for wars to finally and definitively end. Thus, everyone who was able to fight had to constantly be ready for battle. The nobles, especially, spent most of their lives training for war. Whenever a war broke out, it was their duty to show off their skills. If they didn’t want to fight, they had to pay the king a large amount of money to avoid battle.
Of course, the vast majority of people in the Middle Ages didn’t have enough money to buy their way out of the conflict. So they could be forced to join the army through conscription. If you owned any land, you could be summoned to provide soldiers for the war effort. The more land you had, the more soldiers were expected from you. The poor peasants, who had little or no military training, were usually the ones sent into battle by these powerful landowners. They were led by a knight or two who tried their best to bring some order to the chaos.
Some leaders recognized that having a well-trained and organized peasant army could be helpful in a fight. However, the rulers were also afraid that if these peasants became too skilled, they might rebel and try to overthrow them. This back-and-forth was the central tension around military might throughout the difficult Middle Ages.[3]
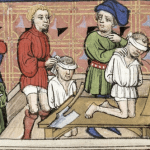
7 The Cruelty of Crime
During the Middle Ages, violent criminals and thieves faced severe consequences if caught. And there were numerous petty problems that received cruel and unusual punishments too. Being a vagrant or getting caught begging was against the law in most European locales. Peasants were forbidden to marry without their lord’s permission. And in some places, women could even be punished for gossiping too much! Surprisingly, even playing football became illegal in England in 1314. Thankfully for our British friends, that didn’t last long.
In the early part of the Middle Ages, determining guilt or innocence involved a brutal practice called trial by ordeal. For example, if a woman was suspected of witchcraft, she might be tied up and thrown into a pool of water. If she survived, people would believe she was innocent. If she died, they assumed she was guilty. Considering she had already been tied up before being thrown in, well, you can guess how many “guilty” witches there were.
As time passed, trial by jury started to replace trial by ordeal from the 1300s onward. However, punishments during this era were still incredibly harsh compared to today’s standards. Public executions were common, as were floggings and beatings. Corporal punishment and forced labor were routinely levied against criminals and evildoers as well. Even petty crimes like thievery and pickpocketing were given harsh retribution.
One of the most dreadful crimes one could commit was high treason. Betraying one’s king was such a heinous act that it resulted in an unimaginably cruel punishment. The condemned person would be tied to a wooden panel and dragged toward execution. They would be hanged, but they would be cut down just before death. Yet there was no mercy in this act. While fully conscious, the person would be disemboweled, and their entrails would be burned before their eyes. Finally, an ax would be swung to sever their head from their body. Then, in what served as a brutal warning to others, their head would be displayed for all to see.[4]
6 Brutal Feudal Life
Life in the Middle Ages was divided into different classes. As has been the case in most eras, those at the top had a pretty good life. They were the ones with power, money, and high status. In most Middle Ages communities, the king technically owned all the land in an area. He would lease it out to noble barons in exchange for an oath of their loyalty. Then, these nobles had the freedom to govern their land and impose taxes as they pleased. As you might expect, they could be brutal.
This privilege for the few landed barons came at a great cost to the serfs. This was the poor mass of people who had no land and no rights. They were essentially treated as slaves by the local nobles. Serfs toiled on the land and brutally worked six days a week from dawn until dusk. Per the feudal system, they were forced to produce crops, raise livestock, and offer some other value to pay their liege lord for the use of the land. And the grind never ended.
In ancient times, it was rare but possible for slaves to rise to powerful positions. Some former slaves became incredibly wealthy and led armies. In one notable instance, the son of a freed slave even became the Emperor of Rome. Sadly for the serfs in the medieval world, such social mobility was unimaginable.
If you were born into the lower class, it was extremely likely you would remain there for your entire life. There was no social mobility or opportunity to work through one’s birth position. Instead, the poor, unwashed masses simply kept working hard and toiling away with no chance of ever improving their lives.[5]
5 Medicine? What Medicine?
Around 540 BC, a Greek doctor named Alcmaeon of Croton introduced a concept that gained popularity in his time. He believed human health depended on the balance of four fluids, known as humors. These humors were blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile. Alcmaeon’s theory was wrong, of course, but it managed to stick around for a thousand years.
By the Middle Ages, medicine hadn’t progressed beyond this point. In some ways, sadly, it had even regressed. Unlike the ancient Greeks—who acknowledged physical causes for illnesses—people in medieval times attributed supernatural reasons to their ailments.
It was quite common for medical examinations to begin with an analysis of the patient’s astrological chart. In many cases, the diagnosis would be an imbalance of the humors. The prescribed treatment involved either bloodletting through cuts or the application of leeches. There were no antibiotics or other medicines, of course. The primitive nature of pain management and symptom care at the time was brutal and unforgiving.
Those who required surgery faced even greater risks. Limited knowledge of the human body’s internal workings hindered progress. Out of fear of superstition and disease, dissecting corpses was prohibited. Moreover, physicians deemed surgery as beneath their profession. That left the task to even less-trained barber surgeons. These individuals were often illiterate and lacked formal scientific know-how. Their only qualification was generally their labor as barbers. Theoretically, then, they knew their way around scissors and (potentially) a scalpel.
The sole available anesthetics were alcohol or certain herbs like mandrake. Shockingly, many surgeons didn’t even employ these methods. They mistakenly believed pain actually aided the healing process. Then, those unlikely few who survived surgery were at substantial risk of infection and subsequent death during the following days and weeks. Sadly, there was no winning in medieval medicine.[6]
4 Work? What Work?
During medieval times, most people lived and worked on farms. Historians now estimate that about 80% of the population tended to the land. However, as towns and cities grew, new job opportunities arose. Sadly, many of these occupations were poorly paid, required a ton of time and effort, and were extremely unpleasant.
One unusual job that became popular was that of a leech collector. The medical profession had a constant need for leeches at the time. So this created an opportunity for people to make a living by gathering the bloodsucking creatures. Catching leeches was not an arduous task, but it was gross. Collectors would simply enter a suitable body of water and wait for the leeches to attach themselves to their bodies.
Another job that offered slightly more income was that of a fuller. Fullers were more common than leech collectors, and they could earn three times as much as a peasant working in the fields. However, being a fuller was far from ideal. Their responsibility was to remove oil, dirt, and other impurities from newly woven cloth. The most effective method they used was stomping on the cloth with their feet inside a barrel filled with human urine. This process would go on for hours and hours, dawn until dusk, six days per week.
As the importance of cities grew through the end of the Middle Ages, more jobs away from the farm took on various levels of significance. Through it all, though, labor protections were nonexistent, and wages were mostly terrible. People had to make the best of the opportunities presented to them, even if they weren’t exactly what they had dreamed of. There simply wasn’t anything better on hand![7]
3 One-Way Worship
During medieval times, the Catholic Church held immense power and influence across Europe. It had great wealth and authority too. For one, it was exempt from taxes. And yet it compelled peasants to pay a tithe of 10% of their earnings to the church. Additionally, peasants were obliged to dedicate their time and labor to the church’s lands without compensation.
The vast resources and political strength of the church allowed it to permeate nearly every aspect of medieval society. Because they had such soft power, worship was essentially forced. After all, who would mount a fight against an organization with that much of an ability to ruin your life?
As the leader of the church and the earthly representative of God, the pope held a level of power that rivaled, and often surpassed, most of Europe’s monarchs. Although popes did not directly command armies, their influence was so significant that they could call for crusades. Those violent wars were fought again and again versus Muslim soldiers across the Holy Lands. Of course, the numerous Crusades have become notorious in history for their extreme bloodshed. Centuries of fierce fighting caused the brutal loss of millions of lives.
In medieval Europe, the Islamic and Christian worlds were largely distinct. The majority of European people were devout Roman Catholics—or at least they claimed to be. However, there were small populations of pagans, Jews, and individuals following other teachings. They just couldn’t be too open about their faith.
These religious minorities faced the constant threat of persecution and death due to their unpopular belief systems. Because of the sheer dominance of the Catholic Church, diversity in religious practices existed at great risk to those who dared to differ. Worship was very power-driven from the top down in the Middle Ages, and if you went against it, you literally risked your life.[8]
2 Woes for Women
Life during the Middle Ages was challenging and unjust in many ways. Sadly, this was particularly true for girls and women. For centuries, they found themselves stuck in a society dominated by men. In those days, women had very limited rights. Until they got married, they were essentially the possessions of their fathers. Once they married, their ownership would transfer to their husbands.
If a woman was attacked, harmed, or killed, the focus would often be on her husband as the unfortunate victim. That was because the husband was seen as the one who suffered the loss or damage to his wife as property. Pregnancy and childbirth were awful too. Women routinely died while giving birth to babies. Without anything close to proper medical knowledge, pregnant women and mothers were at the mercy of fate in an uncaring and cruel world.
Through it all, women were primarily viewed as child bearers and raisers. However, female peasants were still expected to toil in the fields. Sadly, they received much lower pay than men, even though they performed the same labor. Then, after work, they were still expected to do domestic duties and care for children.
Despite these obstacles, a small number of women managed to defy expectations and attain positions of power and influence. In certain instances in England, women were granted special licenses that permitted them to operate their own businesses. They could also inherit wealth under specific circumstances. But those women were the very rare privileged few. For the vast majority of women during the Middle Ages, life was a joyless slog.[9]
1 It Was a Cold, Cold Time to Be Alive
The history of human civilization spans about 6,000 years. Across this journey, humans have been fortunate to experience relatively stable and pleasant temperatures. But not every decade has had it equally easy. Around 1300, a significant drop in the global average temperature occurred. For several centuries, it caused a temperature decline of approximately 2-3 degrees Fahrenheit (1.5 degrees Celsius). That may not seem like a lot, but it lasted a long time. And it was worse in some places (like Europe) than in others. Across northern Europe, cold languished for generations.
This prolonged cooling period was so significant that weather historians now know it as the Little Ice Age. As you might expect, its impact on Medieval Europe and other nearby regions was devastating. Frozen rivers and harbors persisted for months, crops failed, and tens of thousands of people perished due to famine and mass starvation. As if all these other things about living in the Middle Ages weren’t bad enough, the cold was the proverbial icing on a really crappy cake.
Scientists now know the Little Ice Age came from a combination of volcanic eruptions and solar activity. But during the Middle Ages, superstition prevailed. People held what we now consider to be primitive beliefs about the cause of natural phenomena. Some of them attributed these cold weather events to a vengeful God. Others claimed it was the machinations of magic and evil witches. The drastic temperature decline exacerbated religious persecution during the era. In turn, it greatly contributed to the prevalence of witch burnings and mass violence.[10]