Movies and TV
Movies and TV  Movies and TV
Movies and TV  History
History 10 Dirty Government Secrets Revealed by Declassified Files
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Wacky Conspiracy Theories You Will Need to Sit Down For
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Weird Ways That TV Shows Were Censored
 Our World
Our World 10 Places with Geological Features That Shouldn’t Exist
 Crime
Crime 10 Dark Details of the “Bodies in the Barrels” Murders
 Animals
Animals The Animal Kingdom’s 10 Greatest Dance Moves
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Box Office Bombs That We Should Have Predicted in 2025
 History
History 10 Extreme Laws That Tried to Engineer Society
 History
History 10 “Modern” Problems with Surprising Historical Analogs
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Movie Adaptations That Ruined Everything for Some Fans
 History
History 10 Dirty Government Secrets Revealed by Declassified Files
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Wacky Conspiracy Theories You Will Need to Sit Down For
Who's Behind Listverse?

Jamie Frater
Head Editor
Jamie founded Listverse due to an insatiable desire to share fascinating, obscure, and bizarre facts. He has been a guest speaker on numerous national radio and television stations and is a five time published author.
More About Us Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Weird Ways That TV Shows Were Censored
 Our World
Our World 10 Places with Geological Features That Shouldn’t Exist
 Crime
Crime 10 Dark Details of the “Bodies in the Barrels” Murders
 Animals
Animals The Animal Kingdom’s 10 Greatest Dance Moves
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Box Office Bombs That We Should Have Predicted in 2025
 History
History 10 Extreme Laws That Tried to Engineer Society
 History
History 10 “Modern” Problems with Surprising Historical Analogs
10 Ridiculous But Surprisingly Fascinating Scientific Research Studies
Fueled by unquenchable curiosity, some scientists embark on studies that appear to be ridiculous, obvious, or insignificant. These scientists often face criticism and mockery from inside and outside the scientific community. However, if you look closely, this seemingly wacky research is also meaningful and even provocative.
10 Fruit Bats Love Oral Sex

Animals have sex primarily for reproduction rather than pleasure. The male inserts his penis into the female’s vagina, and after a minute or two, the deed is done.
Sex among animals is so basic and boring that it’s fascinating to know that certain mammals engage in sexual activities that are associated with humans and pleasure, such as fellatio and cunnilingus.
In 2009, researchers from the Guangdong Entomological Institute in Guangzhou, China, accidentally discovered that short-nosed fruit bats engage in oral sex. During the study, the scientists expected to see typical animal behavior such as grooming. Instead, they observed that female fruit bats licked the male’s penis during sex.
In another study conducted in 2010 and 2011, researchers discovered that flying foxes (another fruit bat species) engage in oral sex, too. This time, it was the male bat that licked the female’s vagina. In both studies, researchers discovered that engaging in fellatio and cunnilingus prolonged sex among the bats.
Scientists have not yet discovered the evolutionary basis of oral sex among fruit bats. But they suggest that it might help in sperm transportation, stimulation of female glandular secretions, and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases.
9 Cows With Names Produce More Milk
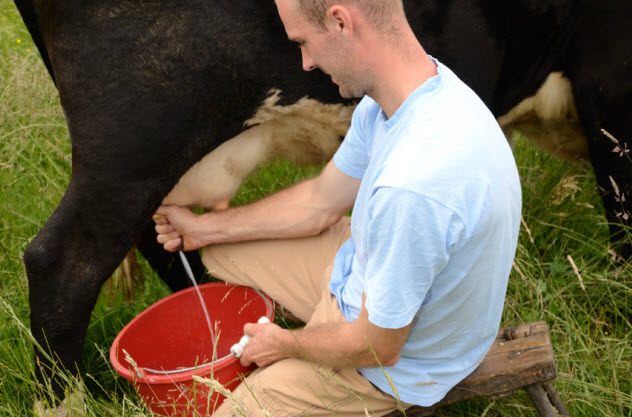

Dairy farmers could potentially increase their incomes with one simple but weird trick—give their cows names. A scientific study published in Anthrozoos suggested that cows with names produce more milk than their nameless counterparts.
This bizarre study was conducted by Drs. Catherine Douglas and Peter Rowlinson of Newcastle University, and it involved over 500 dairy farmers from the United Kingdom.
On average, cows produce 7,500 liters (2,000 gal) of milk over a period of 10 months. But Douglas and Rowlinson discovered that cows with names produced 260 liters (70 gal) more.
Many dairy farmers have long suspected that giving their cattle some “one-to-one attention” increases milk production, but this research was the first that tried to prove it scientifically. According to the study, cows that are herded as a group also produce less milk.
8 Dogs Defecate In A North-South Stance

Several studies suggest that certain animal species—such as birds, foxes, and deer—possess magnetic sensitivity. Inspired by this research, a team of scientists from the Czech Republic decided to find out if dogs possess this amazing ability, too.
The researchers used defecation to determine whether our canine friends adjust their actions according to Earth’s magnetic field. The study involved 70 dogs from 37 breeds. The researchers held the experiment in an open field because dogs can be influenced by familiar surroundings. In total, the dogs defecated almost 1,900 times.
During the experiment, the scientists discovered that dogs prefer to poo “with their bodies aligned in a North-South stance.” They also found that dogs avoid defecating in an East-West alignment.
Interestingly, the dogs would only poo in a North-South stance if the magnetic field was calm. If it wasn’t, then the dogs would defecate in any direction that they preferred.
The scientists also discovered that dogs on leashes didn’t care whether their bodies were aligned with Earth’s magnetic field. Apparently, only canines that roam freely are likely to assume the North-South stance when defecating.
7 Viagra Helps Hamsters Recover Faster From Jet Lag

We all know that Viagra is used to treat erectile dysfunction. However, Diego Golombek of the National University of Quilmes in Buenos Aires, Argentina, has discovered that this light blue pill might also help to treat jet lag.
This bizarre scientific research was conducted on hamsters that were injected with Viagra. After administering the drug, the rodents’ sleep cycles were pushed ahead by six hours—the approximate amount of time needed to fly from New York to Paris.
The hamsters on Viagra recovered from jet lag as much as 50 percent faster than the hamsters without Viagra. Although the results were fairly positive, scientists do not know if the same effect will occur in humans.
Furthermore, Viagra was administered to the hamsters via injection. Scientists are uncertain if taking the drug as a pill will produce the same effect.
6 Night Owls Are More Likely To Become Psychopaths Than Early Birds

Who knew that staying up late at night could potentially make you a psychopath?
According to a study conducted by Dr. Peter Jonason of the University of Western Sydney, people who stay up late have a tendency to manifest antisocial personalities.
After assessing the sleeping patterns of 250 university students, Jonason discovered that night owls are more likely to become narcissistic, psychopathic, and manipulative than early birds.
Jonason believes that there is an “evolutionary basis for the link between antisocial [behavior] and a preference for being awake late at night.” If you look at nature, most predators—like scorpions and lions—are awake at night.
In human society, those who perpetrate crimes and engage in sexual promiscuity are often active during the twilight hours. However, Jonason admits that more research is needed to show a conclusive link between staying up late and the manifestation of antisocial tendencies.
5 Mice With Mismatched Heart Transplants Live Longer When Exposed To Classical Music

Several studies have confirmed that listening to classical music is associated with stress reduction, sleep improvement, and focus enhancement. However, scientific research conducted by Masateru Uchiyama of Juntendo University Hospital in Tokyo suggests that listening to classical music might benefit the heart as well.
Uchiyama’s research involved mice with mismatched heart transplants. The rodents were divided into four groups. One group listened to Verdi’s opera La Traviata. Another group listened to Mozart. The remaining two groups were exposed to Enya and “a range of single monotones,” respectively.
The results of this bizarre experiment were quite remarkable. The group that listened to Verdi’s opera survived for 26 days. The Mozart group lasted for 20 days. The groups of mice exposed to Enya and the single monotones survived 11 and seven days, respectively.
Uchiyama verified the results of his experiment by exposing deaf mice with mismatched heart transplants to Verdi’s opera. Compared to the rodents who had actually heard the song, the deaf mice only lasted seven days.
This result verified Uchiyama’s assumption that actually hearing the music—and not other factors like vibrations—lengthened the survival rate of mice.
4 Expensive Placebos Are More Effective Than Cheap Placebos
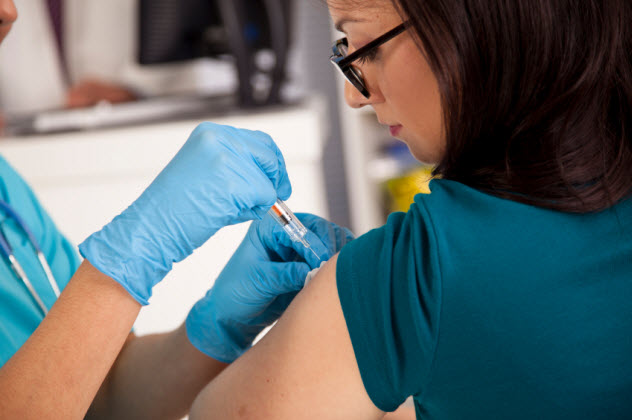
Although the placebo effect is not fully understood, several studies show that this seemingly miraculous phenomenon has the ability to alleviate depression, pain, and other health conditions.
To add to the mystery, scientists recently discovered that expensive placebos are more effective than cheap ones. This intriguing research was conducted on actual patients who were suffering from Parkinson’s disease. The results were published in the journal Neurology.
The researchers informed 12 patients that they were going to get “shots of two formulations of equal effectiveness of the same drug.” The only difference was the cost.
The first formulation cost $1,500, and the second one was $100. In reality, the injections were only saline and didn’t contain any active ingredients. After receiving the $1,500 placebo shots, the majority of patients experienced significant improvement in their motor function. However, when the $100 shots were administered, no notable changes resulted.
When the truth was revealed to the patients, eight admitted that “they expected the expensive drug to be more effective.” The remaining four subjects said that they “had no expectation of greater benefits.”
Interestingly, the patients who did not have any expectations about the expensive placebo were the ones who did not show any significant changes during the study.
3 Wasabi Is An Excellent Fire Alarm

Wasabi is a Japanese condiment that is usually eaten with sushi. Wasabi contains a chemical compound called isothiocyanate, which is the same substance that gives mustard its distinct flavor.
Outside Japan, it’s difficult to find real wasabi. Almost all of the wasabi served in US restaurants is simply a mixture of mustard, food coloring, and horseradish.
Researchers from Shiga University of Medical Science have discovered that this pungent herb can also save lives during catastrophes like fires. Professor Makoto Imai developed a wasabi fire alarm that “sprays out a synthesized wasabi smell” if it detects smoke.
The unconventional fire alarm was tested on 14 people, four of whom were deaf. The results were quite remarkable. All but one subject woke up within two minutes after smelling the pungent wasabi.
The one person who didn’t wake up had a blocked nose. The researchers tried using other plants like lavender and peppermint, but none were as effective as wasabi in waking up people.
2 Bacon Can Cure Nosebleeds
According to a study conducted by Ian Humphreys and his team, bacon can quickly and effectively treat a nosebleed by serving as a nasal tampon. For this bizarre method to work, one must plug the bleeding nostril with a piece of cured pork. The meat must be uncooked.
At Detroit Medical Center, Humphreys and his colleagues tested their bacon hypothesis on a girl who had Glanzmann thrombasthenia, a rare hereditary disease that causes prolonged bleeding. After sticking a piece of cured pork inside the girl’s bloody nose, the bleeding stopped immediately.
The results of this bizarre scientific research were published in the Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology. The researchers acknowledged that doctors had used cured pork to treat nosebleeds in the past. However, the practice was discontinued.
Humphreys and his colleagues speculate that the high risk of acquiring parasitic and bacterial complications from stuffing one’s nose with cured pork caused the unconventional treatment to be abandoned.
1 Diamonds Can Be Created From Tequila

At first glance, you would think that diamonds and tequila don’t have anything in common. But a closer look would show you otherwise. Scientists from the National Autonomous University of Mexico discovered that tequila has a “ratio of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon which lies within the diamond growth region.” This surprising discovery led researcher Javier Morales and his team to create synthetic diamonds from tequila.
During the research, the scientists attempted to create diamonds from acetone, methanol, and ethanol. When they diluted ethanol in water, they discovered that it formed high-quality diamond films. Interestingly, tequila has similar proportions of 60 percent water and 40 percent ethanol, which is the ideal compound for creating synthetic diamonds.
To test their theory, the scientists recreated their experiment with a cheap bottle of white tequila. At first, they were worried that the other components of the alcoholic drink would obstruct or contaminate the process. But they didn’t. Just like the experiment with ethanol and water, tequila produced “spherical-shaped diamonds of nanometric size.”
+ Cats Can Make Humans And Animals Go Crazy

For many of us, cats are more than pets. They’re members of our family. However, a scientific study from Charles University in Prague suggests that cats can alter human and animal behavior.
It’s not the cats per se that cause the problem. Instead, it’s the parasites known as Toxoplasma gondii that live inside their bodies and propagate through their feces.
A study conducted at Imperial College London showed that rats infected with T. gondii lost their fear of cat odor. The parasite also caused the rats to be attracted to the smell of cat urine.
The rodents were introduced to other animal odors like dogs and minks, but they were only attracted to feline urine. Researcher Joanne Webster coined the term “fatal feline attraction” to describe this bizarre phenomenon.
In humans, the effects of T. gondii range from weird to extremely weird. In the Charles University study, researchers discovered that men infected with T. gondii “were more introverted, suspicious, oblivious to other people’s opinions of them, and inclined to disregard rules.”
On other hand, women infected with the parasite “were more outgoing, trusting, image-conscious, and rule-abiding.” The researchers also found that infected people became less attentive and “had significantly delayed reaction times.”
But the most alarming and bizarre effect of T. gondii on humans is that it can potentially cause schizophrenia.
When not busy working with MeBook—an app that transforms your Facebook into an actual printed book—Paul Jongko spends his time writing interesting stuff and creating piano covers.