 Animals
Animals  Animals
Animals  Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Box Office Bombs That We Should Have Predicted in 2025
 History
History 10 Extreme Laws That Tried to Engineer Society
 History
History 10 “Modern” Problems with Surprising Historical Analogs
 Health
Health 10 Everyday Activities That Secretly Alter Consciousness
 History
History Top 10 Historical Disasters Caused by Someone Calling in Sick
 Animals
Animals 10 New Shark Secrets That Recently Dropped
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Forgotten Realities of Early Live Television Broadcasts
 Technology
Technology 10 Stopgap Technologies That Became Industry Standards
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Wild Facts About Taxidermy That You Probably Didn’t Know
 Animals
Animals The Animal Kingdom’s 10 Greatest Dance Moves
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Box Office Bombs That We Should Have Predicted in 2025
 History
History 10 Extreme Laws That Tried to Engineer Society
Who's Behind Listverse?

Jamie Frater
Head Editor
Jamie founded Listverse due to an insatiable desire to share fascinating, obscure, and bizarre facts. He has been a guest speaker on numerous national radio and television stations and is a five time published author.
More About Us History
History 10 “Modern” Problems with Surprising Historical Analogs
 Health
Health 10 Everyday Activities That Secretly Alter Consciousness
 History
History Top 10 Historical Disasters Caused by Someone Calling in Sick
 Animals
Animals 10 New Shark Secrets That Recently Dropped
 Movies and TV
Movies and TV 10 Forgotten Realities of Early Live Television Broadcasts
 Technology
Technology 10 Stopgap Technologies That Became Industry Standards
 Weird Stuff
Weird Stuff 10 Wild Facts About Taxidermy That You Probably Didn’t Know
10 Odd Things You Probably Didn’t Know About Yourself
We’ve all heard the phrase “I know this place like the back of my hand.” It expresses ultimate familiarity, the idea that you know an area as well as your own body.
SEE ALSO: 10 ‘Facts’ About The Human Body That Are Completely False
But your body might beg to differ. For as much as we think we’ve got a handle on the skin suit we spend all day strolling around in, the truth is it’s capable of lobbing some strange surprises. Think you know yourself? Think again.
10Your Body Probably Isn’t The Shape You Think It Is
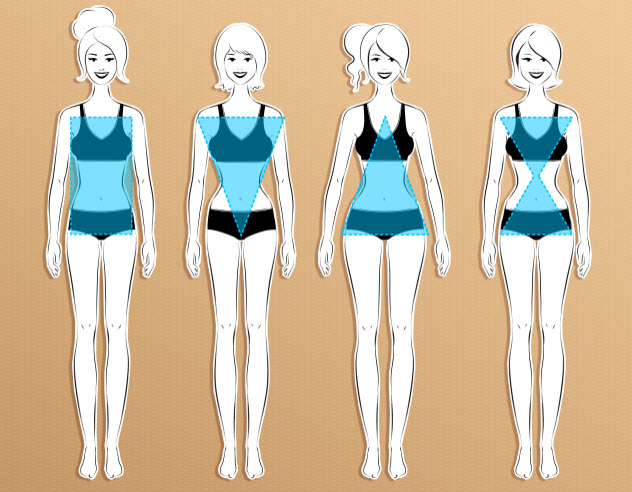
Humans come in a fascinating range of shapes and sizes. You might be shaped like a beach ball, a pear, a masculine V, an hourglass, or something else entirely. Good luck telling someone else what that shape is if you’re female. A 2014 study by Manchester Metropolitan University (MMU) found that only 10 percent of British women could correctly identify their body shape.
Female bodies tend to come in five varieties. There are pears (big butt, small bust), spoons (big bust, small butt), rectangles (similar bust, waist, and shoulder size), and triangles/inverted triangles. Then there’s the hourglass—the curvy figure of Jessica Rabbit and a thousand teenage fantasies. The hourglass is meant to be the pinnacle of femininity. It’s the body shape most female clothes are cut for. It’s also a shape that remarkably few women can lay claim to.
Although more women in the MMU study classified themselves as hourglasses than any other figure, the results said something different. Among women aged 18–35, only 30 percent fell into that category. For those over 35, the figure fell to just 4 percent. Taken overall, roughly 13 percent of women were hourglasses, compared to the 26 percent who thought they were.
Of the 3,000 women in the study, 63 percent were rectangles. For women over 56 years old, over 80 percent had this body shape. Although it may not be considered classically feminine, it’s a much more common female body shape than any other.
9Your Penis Is Probably Bigger Than You Think It Is

If you’re male, you probably spent an inordinate amount of your teenage years thinking about your junk. Questions about size and shape are so common among guys that “penis anxiety” is a recognized medical term.
Well, you can stop worrying. In early 2015, the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, and Neuroscience in the UK released the results of their global study into penis size. They found that having a wang a mere 13 centimeters (5 in) long would make you bigger than 50 percent of the men in the world.
It turns out that most guys have similar-sized junk. About 94 percent of the population measures between 9.2 centimeters (3.6 in) and 16.4 centimeters (6.5 in) when erect. It’s only at the extremes that you get porno-sized and micro penises. The bigger ones probably have the effect of skewing statistics upward. We’ve all heard that 15 centimeters (6 in) is “average.” In reality, having a 15-centimeter (6 in) schlong means you have a bigger penis than 91 percent of men globally.
If you want to see how you measure up, The Guardian published a handy interactive chart based on the study here. Just please don’t spam the comments section with posts celebrating your Ron Jeremy–sized wang.
8Your Man Boobs Are Basically Just Boobs

Man boobs (aka “moobs”) are the antithesis of everything we love about breasts—the Joker to boobies’ Batman. Largely found on overweight men, they’re a flabby mockery of good, old-fashioned lady breasts.
Or are they? While some moobs really are nothing more than flab, most of them are a lot more solid than that. In most cases, man boobs are basically the exact same thing as the real deal.
The technical term for moobs is “gynecomastia,” which is often caused by the growth of breast tissue. This is a particular problem among overweight men, as fat cells are notorious for flooding our bodies with the female hormone estrogen.
Estrogen is, among other things, the stuff that makes women’s boobs grow in the first place. For men with low testosterone (due to age or just natural levels), this estrogen spike is enough to make them start developing in a similar direction.
It’s not just overweight men who experience this. Thanks to the raging hormonal assault that is adolescence, even skinny male teenagers can sometimes develop the condition.
7Your Height Could Predict Your Life Span

Death is a terrifying fact that every living human will to face. But imagine if you could predict when that day would come. Unbelievably, you might be able to. According to a number of studies, your height could well be an indicator of your life span.
Even though it sounds unlikely, there are real-world examples to back this up. You may have heard of the village of Villagrande Strisaili in Sardinia. The place is famous because it has the highest proportion of centenarians in Europe.
It’s also a famously short place. The average male height of the oldest generation is a tiny 160 centimeters (5’3″). When someone taller does get born into Villagrande Strisaili, researchers say they tend to die up to two years sooner than their shorter counterparts.
It’s not just this village, though. Other studies have suggested a link between being tall and dying prematurely. In one comprehensive example, researchers looked into the height and life span of 1.3 million Spaniards. They discovered that every additional centimeter in height reduced the average life span by 0.7 years. Bad news for basketball players, excellent news for munchkins.
6Your Drunken Behavior Fits Into One Of Four Categories

Official figures put the number of Americans who consume alcohol at least once a year at 70 percent of the adult population. With so many millions of drinkers wandering around, you might assume that the types of drunkenness are as varied as the people themselves.
Science disagrees. According to a 2015 study, your drunken behavior fits into one of only four separate categories. The researchers blessed each category with a catchy, pop culture name.
Someone who acts the same whether drunk or sober is an Ernest Hemingway. An agreeable person who becomes even more agreeable after a tipple is a Mary Poppins. The introverted guy who turns into the life of the party after a few beers is known as the Nutty Professor. Meanwhile, the close friend who turns into a destructive she-devil spewing hellfire in her wake falls under the category of Mr. Hyde.
The gender of our last example wasn’t chosen randomly. The Mr. Hyde group has more women in it than any other and was most closely associated with problem drinking. The Hemingways also suffered with alcohol problems but to a lesser extent.
Amusing as this sounds, the researchers hope their categories will one day help clinicians to identify the root cause of problem drinking. If you’re curious to see where you fall on the scale, the BBC made an interactive test you can take here.
5Giving Birth Can Be Even Harder Than You Think

No one ever said that giving birth was simple. That’s why we say things are “easy as pie,” not “easy as contractions.” Popping a living human out of your crotch is hard work.
It might be even harder than you think. Researchers recently started running MRI scans on women after they gave birth. These types of scans are typically used for sports-related injuries.
The results were crazy. For some women, the damage sustained while giving birth was equivalent to the sort of hard-core injury you might get from running a marathon.
A University of Michigan study identified stress fractures in one-quarter of postpartum women that were similar to those suffered by serious athletes. Approximately 41 percent of these women had pelvic muscle tears. About two-thirds had the sort of injuries you’d associate with severe muscle strain. If you’re one of these women, childbirth is less like a miracle and more like a brutal, injury-inducing workout.
If any male readers are wondering how they would hypothetically fare in labor, here’s a video from a Chinese hospital that allowed 100 men to artificially experience similar levels of pain. Most of them lasted an absolute maximum of five minutes before begging the nurse to make it stop.
4You Can Literally Die Of A Broken Heart

Have you ever lost someone or gone through a devastating breakup? Most of us who have been there know it hurts in a way that physical pain can’t even begin to approach. If it was particularly bad, you might have even felt like you were going to die.
Well, we’ve got some bad news. Although it’s unlikely, sometimes you really can die from a broken heart. This is something we see all the time in the animal kingdom. Extreme emotions—including fear and grief—can trigger stress-related heart attacks that are sometimes fatal.
Adrenaline floods the animal’s body at such a rate that its own blood becomes almost toxic, damaging the heart and other muscles. This phenomenon has been observed in elk, moose, sheep, whales, dolphins, bustards, river otters, and more. It has even been observed in humans.
One famous example happened in 1986. A 44-year-old Massachusetts woman was admitted to the hospital, suffering all the classic symptoms of a heart attack. But doctors found no evidence of coronary heart disease. Later, they determined that the woman’s “heart attack” was likely brought on by the news that her 17-year-old son had committed suicide.
Although that was an extreme case, there are many other examples of sudden, stress-induced heart attacks—and not all are related to grief. During the Persian Gulf War in 1991, the stress of being a possible Iraqi target caused Israeli heart attack rates to spike dramatically.
3Your Face Can Reflect Your Personality

Most of us are taught at a young age not to judge by appearances. Even as adults, this is worth remembering. In 2011, the UK press falsely accused retired teacher Christopher Jefferies of murder on the grounds that he looked weird. For the record, Jefferies was exonerated after someone else confessed to the killing.
So when we say that your face can reflect your personality, we don’t mean that in an absolute sense. Nonetheless, there’s scientific evidence that as you get older, your face betrays previously hidden aspects of you. It’s called the Dorian Gray effect, and it’s weird as all get out.
In one study, researchers noted that women’s faces grew to match the personalities they’d had in earlier life. Those with attractive, sociable personalities were perceived by others to grow in attractiveness as they got older. By their fifties, they were considered far better looking than women who had been born naturally prettier but were less personable.
According to the researchers, this is because more sociable women became better at grooming, using makeup to hide the effects of aging and so on. To an outside observer, they became more attractive.
Equally weird was the effect observed in men. Rather than become better looking, researchers found that men who were naturally attractive became more sociable as they got older. Weirdly, it seems that you can frequently judge a person’s social life purely by how good-looking they appear to be.
2You Can Measure The Darkness Of Your Personality

Everyone has a hint of darkness in them, whether it’s a mild manipulative streak or full-blown psychopathy. The worst of us may have the “dark triad”—the rare combination of narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy that make up the personalities of some of the nastiest people in the world.
Although we doubt that any of our readers suffer from the full triad, most of us would probably be interested to know where we score relative to the general population. Luckily, the BBC is here to help. On their site, they’ve set up a questionnaire to help you discover just how evil you really are.
Although the BBC doesn’t claim the questionnaire is scientific, it’s inspired by real scientific research and uses some of the questions actual researchers use. By saying how strongly you agree or disagree with statements such as “I like to use clever manipulation to get my way” or “make sure your plans benefit you, not others,” you can get a reasonable idea of how high you score on the dark triad. Just please don’t blame us if you discover that you’re secretly a raging psychopath.
1You Could Be One Of The Most Attractive People Alive

Unless we’re utterly deluded, most of us probably have a fairly good idea of how attractive we are. We’re likely aware if our shoulders are too slim to be manly, our legs too stubby to be feminine, or our bellies too large to be hot.
We’ve got some good news. No matter what your body looks like, you’re probably more attractive than you think. Hang around in the right society or time period, and you’d probably be one of the best catches going.
Standards of beauty vary wildly from place to place and across different cultures. Scientists believe this is due to environmental measures rather than evolutionary ones. There is no universal standard of beauty. What we see as average at best in the Western world might be considered the pinnacle of beauty elsewhere.
Take overweight people. Our culture generally views skinnier as better, especially where women are concerned. Go to the Amazon, though, and the opposite is true. Studies show that men of the Tsimane tribe in Bolivia prefer fatter women.
It’s not just weight. Men in our society are usually deemed to be better looking if they have masculine faces and hit the gym regularly. However, research has shown that women in nonurban populations across South America, Asia, and Russia tend to prefer men who look more feminine.
These discrepancies even exist with how specific body parts are viewed. The Himba society of Namibia likes men with long, slender, elegant legs. Western society during the time of Botticelli preferred women with shorter, stubbier ones.
Even with something as simple as race, you can see this effect. You might be an average-looking blond at home, but head to parts of South America and watch the opposite sex swoon over your unusual complexion. In short, no matter how you look, there’s probably someone somewhere who considers you drop-dead gorgeous. Isn’t that nice to know?








